Dispatcher eases workflow implementation
Improve your application’s workflow with the Dispatcher design pattern and XSL
As a developer, you realize that requirements change as a natural part of the application development process. You can best address such change by being prepared. In many applications, workflow — the order in which a process proceeds — experiences frequent changes. In a Java 2 Platform, Enterprise Edition (J2EE) development environment, the Dispatcher design pattern defines a strategy to determine workflow via a separate object. While the Dispatcher pattern, presented in the “J2EE Patterns Catalog,” helps consolidate workflow rules, it can also prove difficult to modify or reuse.
Therefore, application developers would benefit from an easily modifiable and reusable Dispatcher strategy. In this article, you’ll find techniques to develop a dynamic, configurable workflow tool designed to ease workflow development and maintenance, as well as make the user’s experience pleasant.
This article first introduces the Dispatcher pattern, as well as ancillary patterns such as Front Controller and Service to Worker. The article then details an implementation strategy for a reusable dispatcher. It concludes with an example illustrating how a dispatcher can help in a real-world business situation.
Note: This article features example source code.
The Dispatcher design pattern
The Dispatcher design pattern separates view responsibilities from business and system logic, and separates Web production and software development teams. The Dispatcher pattern can meet the following needs:
- Dynamic content generation
- Business logic encapsulation in a camp other than the view
The Dispatcher pattern therefore becomes responsible for view management and navigation. It is best employed when outside resources choose the view. For example, the Service-to-Worker pattern collects data before the dispatcher comes into use so that the dispatcher can choose the view based on the data collected. That scenario contrasts with the typical dispatcher, which chooses the view based on state information; in such a case, the view decides what data to pull.
Solutions
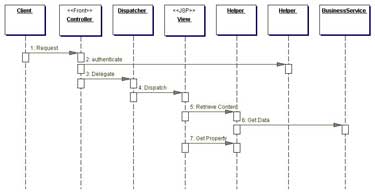
Developers most commonly employ the Dispatcher pattern with a request-handling controller. You could implement the controller with a servlet, a JavaServer Page (JSP), or a component that delegates dispatch responsibilities to the Dispatcher object. Figure 1’s sequence diagram demonstrates the process.

The sequence diagram in Figure 2 illustrates the Service-to-Worker pattern. Notice how it collects the data before the dispatcher performs its tasks.

Strategies
You’ll find many different strategies for implementing a dispatcher. Sun’s “J2EE Patterns Catalog,” proposes several:
- Servlet Front Strategy: A servlet determines workflow using the request, which the servlet then forwards to the appropriate view.
- JSP Front Strategy: A JSP determines workflow, then forwards the request to the view.
- JSP View Strategy: A combination of the JSP Front and the presentation logic. The JSP determines which view to use based on the request; this can be achieved with something as simple as an if statement.
- Servlet View Strategy: Similar to the JSP View Strategy, except it employs servlets.
- JavaBean Helper Strategy: A JavaBean dispatches to the view based on the request.
- Custom Tag Helper Strategy: A tag library dispatches from a JSP.
- Dispatcher in Controller Strategy: The Controller performs the dispatching.
The XSL Dispatcher solution
Next, let’s look at a dispatcher implemented using XML and XSL, in which XSL determines the view. The solution applies XSL to an XML representation of the current session information, along with additional state information such as the current view, the user’s security role, and whatever other information might be handy.
The consequences of using an XSL Dispatcher include:
- An increased level of modifiability
- The ability to reuse views with different workflows
- Reusable workflow API
Implement the strategy
It’s now time to implement the XSL Dispatcher solution. Below, I’ve outlined some of Dispatcher‘s important classes and their responsibilities.
AbstractDispatcherFactory
The abstract AbstractDispatcherFactory class employs the Builder pattern to create dispatchers:
package workflow;
/**
* This class creates AbstractDispatchers.
**/
abstract public class AbstractDispatcherFactory {
public abstract AbstractDispatcher getDispatcher(String name) throws
DispatcherCreateException;
}
AbstractDispatcher
The abstract AbstractDispatcher class dispatches an object. Its next() method determines the next screen in a workflow:
package workflow;
/**
* This class is an abstracted Dispatcher
**/
import java.util.*;
abstract public class AbstractDispatcher {
/**
* The next method finds the next part of a workflow.
* This part of the workflow is represented as a String.
* @returns the name of the next part of the workflow.
**/
public abstract String next(HashMap parameters, Dispatchable ojb,
String current) throws Exception;
public String getDispatcherName() {
return dispatcherName;
}
public String dispatcherName;
}
Dispatchable
The Dispatchable interface represents a dispatchable object. Because it is an interface, you must implement Dispatchable in order for the API to use it:
package workflow;
public interface Dispatchable {
String toXML();
}
DispatcherCreateException
The DispatcherCreateException exception throws if the AbstractDispatcherFactory cannot create a dispatcher:
package workflow;
public class DispatcherCreateException extends Exception {
}
Figure 3 illustrates the relationship between the classes.

Implementation
Next, let’s see how to implement the aforementioned classes.
XMLDispatcherFactory
The XMLDispatcherFactory class creates XMLDispatchers. It retrieves the stylesheet and creates a javax.xml.transform.Transformer useable by the dispatcher:
package workflow.example;
import javax.xml.transform.*;
import org.apache.xalan.processor.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import javax.xml.transform.TransformerConfigurationException;
import javax.xml.transform.stream.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.xml.transform.sax.*;
import java.io.*;
import workflow.*;
/**
* The XMLDispatcherFactor creates instances of XMLDispatchers.
* It reads in the appropriate XSL and
* creates the Transformer object.
*/
public class XMLDispatcherFactory extends AbstractDispatcherFactory {
//The various workflows and the stylesheets associated with them.
static Properties properties = new Properties();
//The Transformer factory
static TransformerFactory factory = new TransformerFactoryImpl();
//Just to keep it simple, add the only workflow we have right now.
static {
properties.put("application", "c:/application.xsl");
System.out.println("added application");
}
public XMLDispatcherFactory()
{
}
/**
* Gets the dispatcher requested and the workflow represented by the name.
* @param name the name of the workflow.
*/
public AbstractDispatcher getDispatcher(String name)
throws DispatcherCreateException {
Transformer transformer = null;
XMLDispatcher dispatcher = null;
try
{
System.out.println("Reading in file");
//Create the transformer object
transformer = factory.newTransformer
(new StreamSource(new FileInputStream
((String)properties.get(name))));
//Create an instance of the XMLDispatcher
dispatcher = new XMLDispatcher(transformer);
}
catch (TransformerConfigurationException transE)
{
System.out.println(transE.getMessage());
throw new DispatcherCreateException();
}
catch (FileNotFoundException noFile)
{
System.out.println(noFile.getMessage());
throw new DispatcherCreateException();
}
dispatcher.dispatcherName = name;
return dispatcher;
}
}
XMLDispatcher
The XMLDispatcher class uses the transformer to determine the next screen. The XMLDispatcher does this by persisting an object to XML before performing the transformation. The class also passes various parameters to the stylesheet. The stylesheet simply produces a string representing the name of the view the user should see next:
package workflow.example;
/* Generated by Together */
import javax.xml.transform.Transformer;
import javax.xml.transform.stream.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import workflow.*;
/**
* The XMLDispatcher uses its transformer to determine workflow
*/
public class XMLDispatcher extends AbstractDispatcher{
public XMLDispatcher(Transformer transformer)
{
this.transformer = transformer;
}
/**
* The implementation of the next method uses XML that represents
* the dispatchable object and the XSL transformation to determine
* the next step in a workflow.
* @param parameters any parameters that need to be handed
* to the transformer by the client
* @param obj the dispatchable object
* @param current the current screen the user is on (that
* keeps this process stateless).
* @return the name of the next step of the workflow
*/
public String next(HashMap parameters, Dispatchable obj,
String current) throws Exception {
transformer.clearParameters();
String next = "";
StringWriter writer = new StringWriter();
//If there aren't any parameters, we'll create our own default ones
if ( parameters == null )
{
parameters = new HashMap();
parameters.put("usercurrent", current);
}
System.out.println(parameters);
System.out.println(obj.toXML());
//Add the parameters to the transformer
Iterator paramKeys = parameters.keySet().iterator();
while (paramKeys.hasNext())
{
String key = (String)paramKeys.next();
transformer.setParameter(key, parameters.get(key));
}
//Perform the transformation
transformer.transform(new StreamSource
(new StringReader(obj.toXML())), new StreamResult(writer) );
next = writer.getBuffer().toString();
//Strip excess information
if ( next.indexOf("?>") > 0 )
next = next.substring(next.indexOf("?>") + 2, next.length());
next = next.trim();
//Return the next screen
return next;
}
private Transformer transformer;
}
The example
To demonstrate the XMLDispatcher in practice, consider the following scenario:
To attract less computer-savvy employment candidates, a company wants to replace its old, complicated Web-based employment application with an easier-to-use form. With its original Web application, candidates filled out an online form at a kiosk at the company’s main office. Candidates, however, complained that the form’s great length and the effort involved in filling it out prompted them to give up in frustration.
To improve the candidate experience, the original single application will be broken into several pages, allowing the candidate to step through them and finally submit her application. Moreover, as a system requirement, the new application must be easily modifiable so it won’t be difficult to add or remove screens. Reusability will also come into play when the company recreates several of its long, Web-based forms.
Based on those considerations, the redesigned employment form’s workflow will be:
- Begin at a start page
- Fill out the demographics
- Fill out felony information
- Fill out work history information
- Sign a legal waver
- View a summary of the submitted information
- Finish
Figure 4 shows the flow graphically.

The XMLDispatcher seems like a good choice to accomplish these goals. However, because it doesn’t possess a Web-based component, one has to be built. In that task, it’s helpful to employ the Front Controller pattern to build a servlet.
With that in mind, the WorkFlowServlet accepts requests from Webpages (as long as they follow a few naming conventions) and then uses the AbstractDispatcher to figure out the next screen. Here’s the code:
package workflow.servlet;
/* Generated by Together */
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import java.beans.Beans;
import java.io.IOException;
import workflow.*;
public class WorkflowServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
// Determine the operation 'add' or 'next'
String operation = req.getParameter("operation");
try
{
System.out.println("applying workflow");
// Get the session.
HttpSession session = req.getSession(true);
// What workflow are they using?
String workflowName = (String)session.getAttribute("workflowName");
// What dispatcher are they using?
AbstractDispatcher dispatcher =
(AbstractDispatcher)session.getAttribute("dispatcher");
// If there isn't already a dispatcher, we'll create one.
if ( dispatcher == null )
{
// We determine what factory to use. To keep it simple,
// we'll let the client tell us.
String factoryName = (String)session.getAttribute("factoryName");
// Get the factory.
AbstractDispatcherFactory dispatcherFactory =
(AbstractDispatcherFactory)Beans.instantiate
(Class.forName(factoryName).getClassLoader(),factoryName);
// Get the dispatcher.
dispatcher = dispatcherFactory.getDispatcher(workflowName);
// Put the dispatcher on the session so it can be used again.
session.setAttribute("dispatcher",dispatcher);
}
// Get the controller.
Controller controller =
(Controller)session.getAttribute("controller");
// If there isn't a controller, create one.
if (controller == null)
{
String controllerName =
(String)session.getAttribute("controllerName");
controller = (Controller) Beans.instantiate
(Class.forName(controllerName).getClassLoader(),controllerName);
session.setAttribute("controller",controller);
}
// Let the controller process the data.
controller.process(req,resp);
// Get the dispatcher.
Dispatchable dispatchable =
(Dispatchable)session.getAttribute("dispatchable");
String nextScreen = new String();
if ( operation.equalsIgnoreCase("next") )
{
// Get the next screen.
nextScreen = dispatcher.next(null,dispatchable,
req.getParameter("current"));
session.setAttribute("nextScreen", nextScreen);
}
else if (operation.equalsIgnoreCase("add")
|| operation.equalsIgnoreCase("remove") )
{
// nextScreen stays the same.
}
System.out.println("The next screen is: " +nextScreen);
// Get the view controller.
String workflowScreen =
(String)session.getAttribute("workflowScreen");
// Go forward onto the view controller.
this.getServletContext().getRequestDispatcher
(workflowScreen).forward(req,resp);
}
catch(ClassNotFoundException ce)
{
ce.printStackTrace();
sendError(resp, ce.getMessage());
}
catch(IOException ioe)
{
ioe.printStackTrace();
sendError(resp, ioe.getMessage());
}
catch(DispatcherCreateException dce)
{
dce.printStackTrace();
sendError(resp, dce.getMessage());
}
catch(ServletException se)
{
se.printStackTrace();
sendError(resp, se.getMessage());
}
catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
sendError(resp, e.getMessage());
}
}
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
doPost(req,resp);
}
private void sendError(HttpServletResponse resp, String message)
{
try
{
resp.sendError(resp.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, message);
}
catch (IOException ioe)
{
ioe.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
The Application
The Application class is a Dispatchable object. The class represents a candidate’s work application filled out on the company Website. The Application includes the candidate’s name, experiences, felonies, and desired position:
package workflow.example;
import java.util.*;
import workflow.*;
/**
* The Application class is a Dispatchable object.
* It holds all the values that make up an Application.
**/
public class Application implements Dispatchable {
public String first = "";
public String last = "";
public Vector felonies = new Vector();
public Vector experiences = new Vector();
public String position = "";
public Date appSubmitDate = null;
/**
* Persist the application to XML
**/
public String toXML() {
StringBuffer buff = new StringBuffer("<application>");
buff.append("<first>"+first+"</first>");
buff.append("<last>"+last+"</last>");
buff.append("<position>"+position+"</position>");
for ( int i = 0; i < experiences.size(); i ++)
buff.append(((Dispatchable)(experiences.elementAt(i))).toXML());
for ( int i = 0; i < felonies.size(); i ++)
buff.append(((Dispatchable)(felonies.elementAt(i))).toXML());
buff.append("</application>");
return buff.toString();
}
}
The Controller
The Application‘s controller is not part of the Dispatcher framework. Rather, it’s a simple object that builds the Application object so that our Dispatcher can process it:
package workflow.example;
/* Generated by Together */
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import workflow.servlet.*;
import java.util.Date;
public class ApplicationController implements Controller {
/**
* This method will process the request and add all the data to
* Application object. It also manipulates the session with
* the appropriate information.
**/
public void process(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
{
// Get Application.
// Add data to Application.
HttpSession session = request.getSession(true);
Application app = (Application)session.getAttribute("dispatchable");
String current = (String)request.getParameter("current");
// Each of these sections of the iff statement represents
// the different screens in the workflow.
if ( current.equals("demographics") )
{
app.first=request.getParameter("firstname");
app.last=request.getParameter("lastname");
app.position=request.getParameter("position");
}
else if ( current.equals("felonies") )
{
Felony felony = new Felony();
felony.description = request.getParameter("description");
System.out.println("#"+felony.description+"#");
if ( felony.description != null && !felony.description.equals("") )
{
System.out.println(request.getParameter("yearCommitted"));
felony.yearCommitted = Integer.parseInt
(request.getParameter("yearCommitted"));
app.felonies.add(felony);
}
}
else if ( current.equals("workhistory") )
{
Experience experience = new Experience();
experience.title = request.getParameter("title");
if ( experience.title != null && !experience.title.equals(""))
{
System.out.println(request.getParameter("startYear"));
experience.startYear = Integer.parseInt
(request.getParameter("startYear"));
experience.endYear = Integer.parseInt
(request.getParameter("endYear"));
experience.employer = request.getParameter("employer");
app.experiences.add(experience);
}
}
else if ( current.equals("legal") )
{
app.appSubmitDate = new Date();//the current date and time
}
else if ( current.equals("start") )
{
}
else if ( current.equals("summary") )
{
}
}
}
application.jsp, seen next, controls the headers and footers to keep everything consistent. For each page in the workflow, the system creates a JSP.
application.jsp
application.jsp becomes a view controller. Dispatcher tells application.jsp what the next view is:
<jsp:directive.page import="workflow.example.*"/>
<jsp:useBean id="dispatchable" class="workflow.example.Application" scope="Session" />
<jsp:useBean id="controller" class="workflow.example.ApplicationController" scope="Session"/>
<% session.setAttribute("workflowName","application");
session.setAttribute("factoryName","workflow.example.XMLDispatcherFactory");
session.setAttribute("workflowScreen","/jsp/application/application.jsp");
%>
<% String nextScreen = (String)session.getAttribute("nextScreen"); %>
<html>
<body>
<bold>My Company's application for employment:</bold>
<form action="/workflowtest/workflow" method=post>
<% if ( nextScreen == null){%>
<jsp:include page="./start.jsp"/>
<%}else{%>
<% pageContext.include(nextScreen); %>
<%}%>
<input type=submit name="operation" value="Next"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Next, you’ll see some other important JSPs.
demographics.jsp
demographics.jsp, inserted in the middle of application.jsp, collects the demographics information. Notice the pageContext.include(nextScreen) above. Here’s the code:
<jsp:useBean id="dispatchable" class="workflow.example.Application" scope="Session" />
<input type=hidden name="current" value="demographics"/>
<table class="legacyTable">
<tr>
<td>First name</td><td><input type=text name="firstname" value="<%=dispatchable.first%>"/></input></td>
<td>Last name</td><td><input type=text name="lastname" value="<%=dispatchable.last%>"/></input></td>
<td>Position</td><td><select name="position"/><option value="IT" <%if ( dispatchable.position.equals("IT") ){ %>selected<%}%>>IT</option><option value="HR" <%if ( dispatchable.position.equals("HR") ){ %>selected<%}%>>HR</option></select></td>
</tr>
</table>
felonies.jsp
On the felonies.jsp screen, the candidate reports any felony convictions. Notice I’ve included an Add button, which contrasts with the way demographics.jsp lets the application.jsp handle the form request:
<jsp:directive.page import="workflow.example.*"/>
<jsp:useBean id="dispatchable" class="workflow.example.Application" scope="Session" />
<input type=hidden name="current" value="felonies"/>
<bold>Please list all the felonies you have committed. If there is more than one hit the add button, when you are finished hit next.</bold>
<table class="legacyTable">
<% int i = 0; %>
<% for ( i = 0; i < dispatchable.felonies.size(); i ++ ) { %>
<tr>
<td>what year?</td><td><%=((Felony)dispatchable.felonies.elementAt(i)).yearCommitted%></td>
<td>desciption</td><td><%=((Felony)dispatchable.felonies.elementAt(i)).description%></td>
</tr>
<%}%>
<tr>
<td>Felony year?</td><td><input type=text name="yearCommitted"/></input></td>
<td>Felony desciption</td><td><input type=text name="description" size=50></input></td>
<td><input type="submit" name="operation" value="Add"/></td><td/>
</tr>
</table>
Next, you see the XSL code, which accepts two parameters. It determines the current screen, and, based on that information, it determines the next screen. The fully qualified path of the next screen is output from the XSL, but the code could be changed to output a looked-up alias instead:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="
<xsl:param name="securityrole">Guest</xsl:param>
<xsl:param name="usercurrent"></xsl:param>
<xsl:template match="/">
<xsl:choose>
<xsl:when test="$usercurrent="start"">
/jsp/application/demographics.jsp
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$usercurrent="demographics"">
/jsp/application/felonies.jsp
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$usercurrent="felonies"">
/jsp/application/workhistory.jsp
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$usercurrent="workhistory"">
/jsp/application/legal.jsp
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$usercurrent="legal"">
/jsp/application/summary.jsp
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$usercurrent="summary"">
/complete.html
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$usercurrent="complete"">
/index.html
</xsl:when>
<xsl:otherwise>/jsp/application/start.jsp</xsl:otherwise>
</xsl:choose>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
When the candidate completes each page, she easily moves to the next page, until, when finished, she submits her application.
Now, imagine that you’ve delivered the application to the company. Let’s say that the HR department desires two changes:
- Because the available positions entail access to highly classified government documents, candidates with prior felony convictions are ineligible, so they don’t need to fill out the work experience section
- The candidates should see a summary of their information prior to final submission to the HR department
To incorporate those new requirements into the workflow, the new XSL code below checks to see if the candidate possesses any prior felony convictions. It also switches the screen to which the legal and summary pages go:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="
<xsl:param name="securityrole">Guest</xsl:param>
<xsl:param name="usercurrent"></xsl:param>
<xsl:template match="/">
<xsl:choose>
<xsl:when test="$usercurrent="start"">
/jsp/application/demographics.jsp
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$usercurrent="demographics"">
/jsp/application/felonies.jsp
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$usercurrent="felonies"">
<xsl:choose>
<xsl:when test="/application[felonies]">
/jsp/application/summary.jsp
</xsl:when>
<xsl:otherwise>
/jsp/application/workhistory.jsp
</xsl:otherwise>
</xsl:choose>
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$usercurrent="workhistory"">
/jsp/application/legal.jsp
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$usercurrent="legal"">
/complete.html
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$usercurrent="summary"">
/jsp/application/legal.jsp
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$usercurrent="complete"">
/index.html
</xsl:when>
<xsl:otherwise>/jsp/application/start.jsp</xsl:otherwise>
</xsl:choose>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
The scenario presented above is a simple one, but it includes common problems developers face everyday.
Other considerations
Workflow not only proves difficult to implement; it also is commonly changed. To mitigate such challenges, the simple API presented here encapsulates workflow in a set of objects. Moreover, it represents workflow as XSL so any object represented as XML can be employed.
As good as the API is, it doesn’t address such other workflow issues as data validation or error handling. Further, as a stateless API, it requires information about the candidate’s location before it determines where to go. A stateful implementation would prove advantageous because the candidate could see a history of her work, as well as an idea of how much remains to be completed. Moreover, the API does not persist the workflow state, so the candidate cannot easily return to her spot in the workflow.
Using XSL to encapsulate business rules provides a strong mechanism for managing workflow. Indeed, it provides a language-independent, extensible solution. As alternatives, you could encapsulate the workflow in a JavaBean or an XML document. However, a JavaBean requires recompilation, and XML doesn’t provide such language-level constructs as sequential-, iterative-, or decision-based processing.
Business rules are written and rewritten. Users always want the greatest possible experience. Developers want manageability, modifiability, and extensibility. In order to meet these needs, it is important to build an API that addresses all the varying issues at once, and incorporates them into the design.