The Internet of Things (IoT) rapidly transforms how businesses interact with customers and deliver value. By connecting everyday objects to the internet, companies can gather valuable data, personalize experiences, and build stronger customer relationships. With the rapid evolution of all digital technology, communications, hardware, software, and IoT mobile app development services are now becoming affordable to many businesses.
Just in my own home, I now have over 40 IoT devices connected and communicating with the cloud, including my doorbell, security cameras, garage door, washer and dryer, dishwasher, vacuum, oven, stove vent, thermostat, smart televisions, smart speakers, and an array of smart plugs and switches. Each of those companies has an invisible connection with me that can be utilized to improve my customer experience (CX) with their brand… providing limitless opportunities for engagement, loyalty, and even upsells.
This article explores the diverse applications of IoT across various industries, highlighting real-world examples and demonstrating how this technology can be leveraged to drive customer loyalty, enhance experiences, and ultimately build value.
Table of Contents
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a vast network of interconnected devices embedded with sensors, software, and network connectivity. This enables these things to collect and exchange data, creating a web of intelligent objects that can communicate with each other and humans. Think of it as giving everyday objects a digital voice, allowing them to share information and respond to commands.
It’s important to remember that IoT is more than just smart home gadgets or wearable tech. While IoT encompasses a wide range of devices and applications, it’s essential to distinguish it from traditional computing devices and simpler communication technologies.
While devices like standard computers, laptops, fixed phones, cell phones, and consumer tablets connect and may control IoT devices, they are not classified as IoT. These devices are primarily designed for general-purpose human-computer interaction rather than the specialized data collection, automation, and analysis that characterize IoT. They function as independent units with humans, whereas IoT devices often operate autonomously or with minimal human intervention within a more extensive network.
Similarly, simple one-directional communication technologies like RFID and NFC are not generally classified as IoT. While these technologies enable data transfer, they typically involve a one-way flow of information, such as scanning an RFID tag to retrieve product information. IoT, on the other hand, emphasizes two-way communication and data exchange between devices, facilitating more complex interactions and automated responses.
IoT is a pervasive technology with applications across all sectors, from agriculture and healthcare to manufacturing and retail. This distinction helps to clarify IoT’s unique characteristics and its focus on interconnected networks of devices that gather and exchange data to drive intelligent actions and improve processes.
The Growth of IoT
While the initial hype surrounding IoT may seem to have settled, the reality is that the industry is experiencing unprecedented growth, exceeding expectations and transforming the technological landscape in profound ways.
Several key factors fuel this expansion:
- Decreasing Costs: The cost of implementing IoT solutions is steadily declining, making it more accessible to businesses of all sizes. Sensors, connectivity modules, and data processing platforms are becoming more affordable, enabling broader adoption across various industries.
- Technological Advancements: IoT devices are becoming increasingly sophisticated, with enhanced capabilities and improved performance. Frameworks and protocols also evolve, enabling seamless integration and interoperability between devices and platforms.
- Cloud Computing Support: Major cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform are heavily invested in IoT, offering robust infrastructure, scalable platforms, and comprehensive services to support IoT deployments.
Even with macroeconomic headwinds, including inflation, rising interest rates, and geopolitical uncertainties, the IoT market continues its upward trajectory.
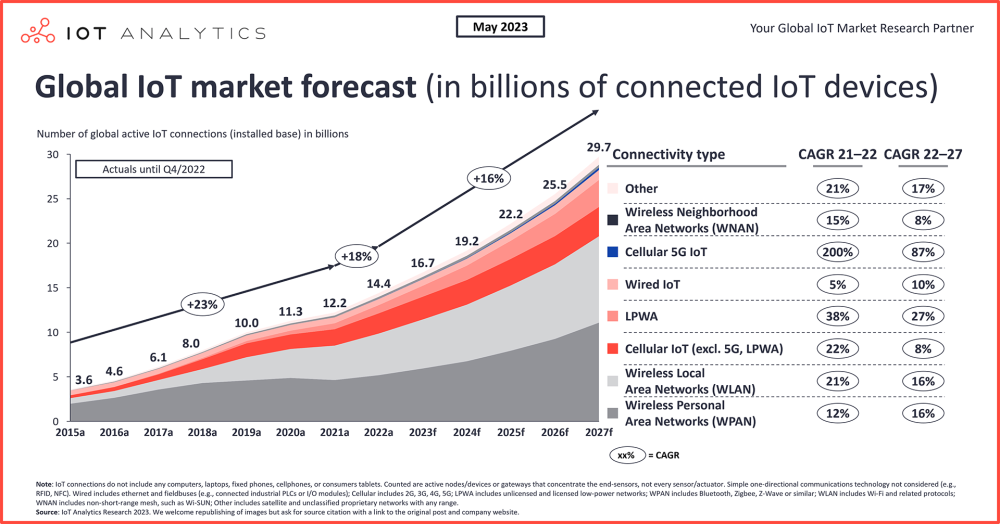
There were 16.6 billion connected IoT devices by the end of 2023, representing a 15% increase over 2022. While growth is expected to moderate slightly to 13% in 2024, reaching 18.8 billion connected devices, the long-term outlook remains exceptionally strong.
Importantly, enterprise adoption of IoT remains robust. Despite economic challenges, 51% of enterprise IoT adopters plan to increase their IoT budget in 2024, with 22% expecting a budget increase of 10% or more compared to 2023. This indicates a continued commitment to leveraging IoT for business transformation and competitive advantage.
The growth of IoT is far from over. As technology advances and costs fall, we can expect even more explosive growth in the years to come, with profound implications for businesses, consumers, and society.
Key Components of IoT
The Internet of Things is a complex ecosystem with interconnected parts working together. Let’s examine the main components that make IoT possible.

Devices: The “Things” in IoT
At the heart of the IoT are the things themselves – the physical devices embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity. These devices come in a staggering variety of shapes and sizes. Some are tiny, like the micro sensors found in medical implants or wearables, while others are massive, like the sensors embedded in aircraft engines for performance monitoring. The trend towards miniaturization is constantly pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, enabling smaller, less intrusive devices to be deployed in new and innovative ways.
These devices range from a few dollars for simple sensors to thousands for sophisticated industrial equipment. Fortunately, the cost of IoT technology is generally decreasing, making it more accessible to businesses and individuals alike.
A crucial aspect of IoT devices is their ability to transmit data. They achieve this through various communication technologies, depending on the application and requirements:
- Short-range technologies like Bluetooth, Zigbee, and Z-Wave are commonly used for communication between devices in close proximity, such as within a smart home.
- Long-range technologies like Wi-Fi and cellular networks enable devices to connect over greater distances, making them suitable for asset tracking and environmental monitoring applications.
- Low-power wide-area networks (LPWANs), such as LoRaWAN and Sigfox, are designed for long-range, low-power communication, making them ideal for connecting remote sensors in applications like agriculture and smart cities.
Many IoT devices are also designed for low power consumption, often operating on batteries for extended periods. This is essential for devices deployed in remote or hard-to-reach locations where replacing batteries frequently is impractical.
Connectivity: Bridging the Physical and Digital Worlds
Connectivity is the glue that holds the IoT ecosystem together. It enables devices to communicate with each other and central systems, allowing for data exchange and coordination. This communication can occur through wired connections, like Ethernet, or wirelessly, using Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks. Wireless connectivity is often preferred due to its flexibility and ease of deployment.
Different network protocols are used for different IoT applications, each with its strengths and weaknesses in terms of range, bandwidth, and power consumption. Choosing the right protocol is crucial for ensuring reliable and efficient communication.
Security is also paramount in IoT connectivity. With billions of devices exchanging data, protecting this information from unauthorized access and cyberattacks is critical. Encryption and authentication mechanisms are essential for ensuring data integrity and confidentiality.
Data Processing: Turning Data into Insights
Data processing is where the true power of IoT lies. Raw data collected by devices is transformed into meaningful insights that can be used to optimize processes, improve decision-making, and create new value.
- Edge computing is a growing trend in IoT. This approach processes data closer to the source, either on the device itself or on a nearby gateway. This reduces latency, improves response times, and minimizes the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to the cloud.
- Cloud computing plays a crucial role in IoT by providing scalable resources for storing, processing, and analyzing massive volumes of data. Cloud platforms offer various services, including databases, analytics tools, and machine learning algorithms, that enable businesses to extract valuable insights from their IoT data.
User Interface: The Human Connection
The user interface bridges the IoT system and the human user. It allows people to interact with devices, monitor data, and control the system.
Mobile Apps
Mobile applications are a popular way to interact with IoT devices. They provide a convenient and user-friendly interface for controlling smart home devices, tracking fitness data, and receiving notifications.
Web Dashboards
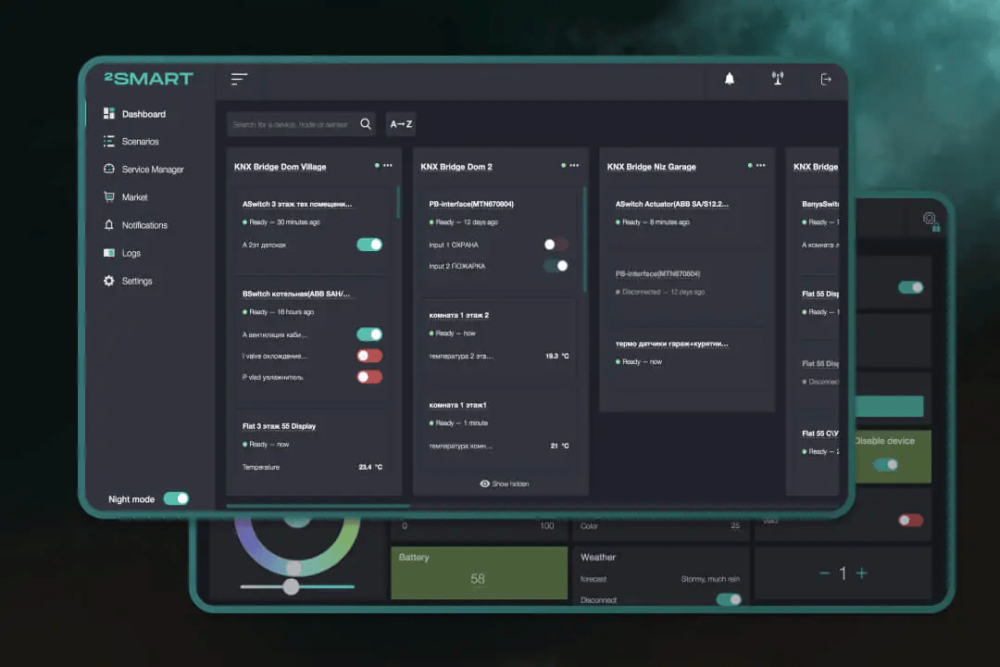
Visually represent IoT data, allowing users to monitor trends, analyze performance, and manage devices from a central location.
Voice Assistants
Voice assistants or smart speakers are increasingly used to interact with IoT devices, particularly in smart homes. Voice control provides a natural and intuitive way to control devices and access information.
By understanding these key components and how they work together, businesses can harness the power of IoT to transform their operations, create new products and services, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
IoT Applications Across Industries
Let’s explore how IoT is being applied in various sectors to drive customer value and loyalty:
| Industry | Example | Value | Marketing Tie-In |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Universal ecosystem for managing and maintaining EV Charging stations | Streamlined charging station management, improved maintenance efficiency, enhanced user experience | Green energy initiatives, charging network reliability, seamless user experience |
| Building Management | Intelligent IoT Building Automation System – Architecture framework for IoT business implementation | Integrated building control, energy optimization, improved occupant comfort, automated facility management | Smart building solutions, energy efficiency programs, modern workplace experience |
| Energy | Mobile app for remote monitoring and maintenance of industrial heat pumps | Remote monitoring capabilities, predictive maintenance, improved efficiency, real-time performance data | Energy efficiency metrics, remote management benefits, preventive maintenance programs |
| HVAC | Smart Automated A/C Drain Line Cleaner – IoT solution for automated HVAC maintenance with software & firmware development | Reduced maintenance costs, prevented water damage, extended equipment life, automated cleaning processes | Preventive maintenance packages, cost savings calculations, equipment longevity guarantees |
| IoT PaaS | IoT cloud platform – Full-fledged IoT site for vendors and businesses launching IoT projects | Rapid IoT deployment, scalable infrastructure, unified device management, data analytics | Platform-as-a-service offerings, IoT solution enablement, digital transformation services |
| Security | Cloud-based access control system with SaaS model and private instances | Flexible access management, enhanced security, scalable deployment options, remote administration | Security-as-a-service offerings, customizable access solutions, enterprise security packages |
| Smart Homes | Home Automation System | Integrated home control, automated routines, enhanced comfort and convenience, energy management | Smart home packages, lifestyle automation solutions, energy optimization services |
Data Collection and Customer Experience
IoT devices act as data collection points, capturing valuable information about customer behavior, preferences, and environmental factors. This data can be analyzed to gain insights into customer needs and optimize the customer journey.
- Personalization: IoT data enables personalized experiences, such as tailored product recommendations, automated actions based on preferences, and proactive service interventions.
- Customer Journey Optimization: By understanding how customers interact with products and services, companies can identify pain points and optimize the customer journey across all touchpoints.
Real-time behavioral triggers form the foundation of modern IoT-driven customer experiences. These systems continuously monitor and react to customer interactions, from motion sensors activating personalized in-store displays to usage patterns triggering maintenance alerts. The sophistication extends to location-based services and environmental adaptations, creating a responsive ecosystem that anticipates and meets customer needs.
Integration across the customer journey has become seamless through sophisticated IoT implementations. Cross-device behavior tracking enables consistent experiences across multiple touchpoints, while real-time journey mapping helps companies understand and optimize every interaction. Automated journey orchestration systems use trigger events to guide customers through personalized paths, with predictive next-best-action recommendations ensuring optimal engagement at each step.
The optimization of these systems requires continuous refinement through strategies like A/B testing of automated responses and machine learning-driven journey optimization. Dynamic resource allocation ensures efficient service delivery, while automated experience personalization creates scalable yet individualized customer interactions.
Advanced analytics are crucial in making sense of the vast amount of IoT data collected. Through multi-device correlation analysis and behavioral cohort segmentation, companies can identify patterns and trends that would be impossible to detect manually. Usage pattern clustering and anomaly detection enable proactive intervention, while sentiment analysis derived from IoT interactions provides deeper insight into customer satisfaction.
Predictive AI has transformed how companies utilize IoT data, enabling them to forecast future customer needs accurately. AI models can predict everything from product failures to potential customer churn by analyzing purchase patterns, usage behaviors, and interaction histories. This predictive capability allows businesses to shift from reactive to proactive customer service, addressing issues before they impact the customer experience.
Building Customer Loyalty and Value
IoT data empowers businesses to build stronger relationships with their customers by:
- Enhancing the Customer Experience: Creating seamless, personalized, and engaging experiences across all channels.
- Providing Proactive Service and Support: Anticipating customer needs, proactively addressing issues, and providing timely support.
- Creating Personalized Loyalty Programs: Tailoring rewards and incentives to individual customer preferences and behaviors.
- Building Trust and Transparency: Communicating clearly about data usage and providing customers with control over their data.
Finding the right IoT development partner is about more than just technical capability – it’s about finding a team that truly understands your business objectives and can translate them into meaningful solutions. From my experience leading enterprise IoT initiatives, companies often focus too narrowly on devices while overlooking the broader ecosystem of data, security, and user experience. The right partner brings not just technical expertise, but the strategic insight needed to turn IoT investments into tangible business outcomes. They should guide you through the entire journey while ensuring your infrastructure remains future-proof and adaptable.
Kostiantyn Oliynyk, Head of IoT at WebbyLab
The Internet of Things is revolutionizing customer engagement. By leveraging the power of connected devices and data analytics, businesses can create personalized experiences, build stronger relationships, and drive customer loyalty. As IoT technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications to further transform how companies interact with their customers.
Explore the potential of IoT to enhance your customer engagement strategies and drive business value.